彼此熟识的最早时间
难度:
标签:
题目描述
代码结果
运行时间: 26 ms, 内存: 16.4 MB
/*
* LeetCode 1101: The Earliest Moment When Everyone Become Friends
*
* Problem statement: Given a list of logs, where each log entry is a triplet (timestamp, person1, person2),
* representing that person1 and person2 became friends at that timestamp. We are to find the earliest
* time at which all people became friends. If there is no such time, return -1.
*
* Approach using Java Streams:
* 1. We will use the union-find (disjoint-set) data structure to keep track of connected components (groups of friends).
* 2. Use streams to sort the logs based on the timestamps.
* 3. Iterate over the sorted logs and union the sets of the two persons in each log.
* 4. After each union operation, check if all persons are in the same connected component.
* 5. If they are, return the current timestamp. If we finish processing all logs and they are not all connected, return -1.
*/
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class Solution {
public int earliestAcq(int[][] logs, int N) {
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(N);
return Arrays.stream(logs) // Step 2
.sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(log -> log[0]))
.filter(log -> {
uf.union(log[1], log[2]);
return uf.getCount() == 1; // Step 4
})
.findFirst() // Step 3
.map(log -> log[0]) // Step 5
.orElse(-1); // Step 5
}
class UnionFind {
private int[] parent;
private int[] rank;
private int count;
public UnionFind(int n) {
parent = new int[n];
rank = new int[n];
count = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
rank[i] = 1;
}
}
public int find(int p) {
if (p != parent[p]) {
parent[p] = find(parent[p]); // Path compression
}
return parent[p];
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP != rootQ) {
if (rank[rootP] > rank[rootQ]) {
parent[rootQ] = rootP;
} else if (rank[rootP] < rank[rootQ]) {
parent[rootP] = rootQ;
} else {
parent[rootQ] = rootP;
rank[rootP]++;
}
count--;
}
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
}解释
方法:
此题解采用了并查集数据结构来解决问题。题目要求找到所有人都相识的最早时间。解题思路如下:首先对事件按时间排序,保证我们按时间顺序处理每对相识的人。使用一个并查集来管理并跟踪每个人的连通性,每个人最初指向自己,表示各自为一个独立的组。对于每个事件,我们使用 union 操作来合并两个人所在的组。如果两个人已经在同一个组里,那么他们已经是间接或直接相识的。如果通过 union 操作后,所有人都属于同一个组(计数器 cnt 为 1),则返回当前事件的时间,表示这是所有人都彼此相识的最早时间。如果遍历完所有事件后,人们仍不全都相识,则返回 -1。
时间复杂度:
O(m log m)
空间复杂度:
O(n)
代码细节讲解
🦆
为什么在处理这个问题时选择使用并查集而不是其他数据结构,比如图的遍历方法?
▷🦆
在合并两个组的操作中,你选择将一个组的根指向另一个组的根,这种选择是否总是有效,或者说是否有可能影响并查集的平衡性?
▷🦆
如果在所有事件处理完之后还有人不相识(返回-1),这是否意味着输入数据中有人从未出现在任何相识事件中?
▷相关问题
省份数量
有 n 个城市,其中一些彼此相连,另一些没有相连。如果城市 a 与城市 b 直接相连,且城市 b 与城市 c 直接相连,那么城市 a 与城市 c 间接相连。
省份 是一组直接或间接相连的城市,组内不含其他没有相连的城市。
给你一个 n x n 的矩阵 isConnected ,其中 isConnected[i][j] = 1 表示第 i 个城市和第 j 个城市直接相连,而 isConnected[i][j] = 0 表示二者不直接相连。
返回矩阵中 省份 的数量。
示例 1:
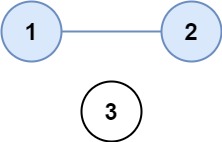
输入:isConnected = [[1,1,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,1]] 输出:2
示例 2:
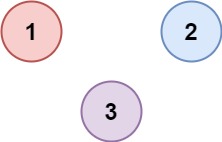
输入:isConnected = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]] 输出:3
提示:
1 <= n <= 200n == isConnected.lengthn == isConnected[i].lengthisConnected[i][j]为1或0isConnected[i][i] == 1isConnected[i][j] == isConnected[j][i]