查询后矩阵的和
难度:
标签:
题目描述
You are given an integer n and a 0-indexed 2D array queries where queries[i] = [typei, indexi, vali].
Initially, there is a 0-indexed n x n matrix filled with 0's. For each query, you must apply one of the following changes:
- if
typei == 0, set the values in the row withindexitovali, overwriting any previous values. - if
typei == 1, set the values in the column withindexitovali, overwriting any previous values.
Return the sum of integers in the matrix after all queries are applied.
Example 1:
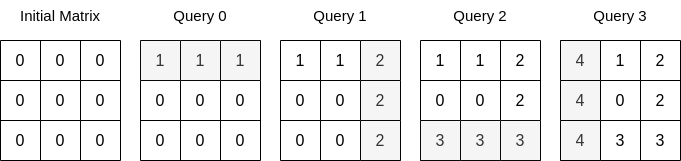
Input: n = 3, queries = [[0,0,1],[1,2,2],[0,2,3],[1,0,4]] Output: 23 Explanation: The image above describes the matrix after each query. The sum of the matrix after all queries are applied is 23.
Example 2:
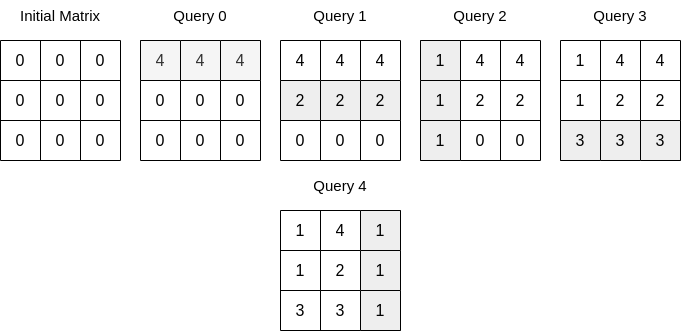
Input: n = 3, queries = [[0,0,4],[0,1,2],[1,0,1],[0,2,3],[1,2,1]] Output: 17 Explanation: The image above describes the matrix after each query. The sum of the matrix after all queries are applied is 17.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1041 <= queries.length <= 5 * 104queries[i].length == 30 <= typei <= 10 <= indexi < n0 <= vali <= 105
代码结果
运行时间: 103 ms, 内存: 33.9 MB
/*
* Problem: Given an integer n and a 2D array queries, where queries[i] = [type_i, index_i, val_i].
* Initially, you have an n x n matrix with all elements as 0.
* For each query:
* - If type_i == 0, update all elements in row index_i to val_i.
* - If type_i == 1, update all elements in column index_i to val_i.
* After all queries, return the sum of all elements in the matrix.
*/
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public static int matrixSum(int n, int[][] queries) {
int[][] matrix = new int[n][n];
Arrays.stream(queries).forEach(query -> {
int type = query[0];
int index = query[1];
int value = query[2];
if (type == 0) {
Arrays.fill(matrix[index], value);
} else if (type == 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
matrix[i][index] = value;
}
}
});
return Arrays.stream(matrix).flatMapToInt(Arrays::stream).sum();
}
}
解释
方法:
本题解采用了一种避免直接构建和修改矩阵的优化方法。首先初始化两个集合 hang 和 lie,分别用来记录所有已被修改过的行和列。同时,用一个变量 ans 来累计矩阵中所有元素的和。遍历查询数组 queries,从后向前处理每个查询,判断当前查询的类型(修改行或列)。如果是修改行且此行未被修改过,则将该行所有元素加上新值,但要减去已被修改的列中对应的元素。同理,如果是修改列且此列未被修改过,则将该列所有元素加上新值,但要减去已被修改的行中对应的元素。这种方法有效避免了重复计算已被修改过的行或列,每次修改只考虑新增加的部分。
时间复杂度:
O(m)
空间复杂度:
O(n)
代码细节讲解
🦆
为什么要从后向前处理查询数组 queries 而不是从前向后?
▷🦆
在处理行或列的修改时,如何确保已修改的列或行中的元素不被重复计算?
▷🦆
当一个行或列被多次修改时,这种算法如何处理以保证最终的矩阵和是正确的?
▷🦆
在遍历 queries 的过程中,使用了两个集合 hang 和 lie 来跟踪哪些行和列被修改过。这种方法在处理极大的 queries 时效率如何?
▷