查询树中环的长度
难度:
标签:
题目描述
You are given an integer n. There is a complete binary tree with 2n - 1 nodes. The root of that tree is the node with the value 1, and every node with a value val in the range [1, 2n - 1 - 1] has two children where:
- The left node has the value
2 * val, and - The right node has the value
2 * val + 1.
You are also given a 2D integer array queries of length m, where queries[i] = [ai, bi]. For each query, solve the following problem:
- Add an edge between the nodes with values
aiandbi. - Find the length of the cycle in the graph.
- Remove the added edge between nodes with values
aiandbi.
Note that:
- A cycle is a path that starts and ends at the same node, and each edge in the path is visited only once.
- The length of a cycle is the number of edges visited in the cycle.
- There could be multiple edges between two nodes in the tree after adding the edge of the query.
Return an array answer of length m where answer[i] is the answer to the ith query.
Example 1:
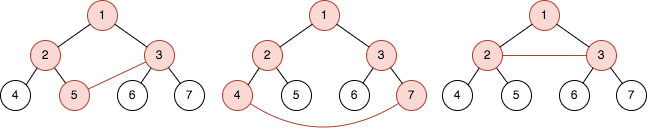
Input: n = 3, queries = [[5,3],[4,7],[2,3]] Output: [4,5,3] Explanation: The diagrams above show the tree of 23 - 1 nodes. Nodes colored in red describe the nodes in the cycle after adding the edge. - After adding the edge between nodes 3 and 5, the graph contains a cycle of nodes [5,2,1,3]. Thus answer to the first query is 4. We delete the added edge and process the next query. - After adding the edge between nodes 4 and 7, the graph contains a cycle of nodes [4,2,1,3,7]. Thus answer to the second query is 5. We delete the added edge and process the next query. - After adding the edge between nodes 2 and 3, the graph contains a cycle of nodes [2,1,3]. Thus answer to the third query is 3. We delete the added edge.
Example 2:
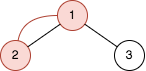
Input: n = 2, queries = [[1,2]] Output: [2] Explanation: The diagram above shows the tree of 22 - 1 nodes. Nodes colored in red describe the nodes in the cycle after adding the edge. - After adding the edge between nodes 1 and 2, the graph contains a cycle of nodes [2,1]. Thus answer for the first query is 2. We delete the added edge.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 30m == queries.length1 <= m <= 105queries[i].length == 21 <= ai, bi <= 2n - 1ai != bi
代码结果
运行时间: 91 ms, 内存: 45.9 MB
/*
* 思路:
* 使用Java Stream进行同样的操作,简化代码。
*/
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public int[] cycleLengths(int n, int[][] queries) {
return Arrays.stream(queries)
.mapToInt(query -> findCycleLength(query[0], query[1]))
.toArray();
}
private int findCycleLength(int a, int b) {
int length = 0;
while (a != b) {
if (a > b) {
a /= 2;
} else {
b /= 2;
}
length += 1;
}
return length + 1; // 加上公共祖先节点的长度
}
}
解释
方法:
这个题解利用了完全二叉树的性质和位运算来找到从一个节点到另一个节点的路径。对于每个查询,首先确定两个节点中的较大值作为a,较小值作为b。然后计算a和b的二进制表示的长度差,这个长度差l代表了a相对于b在树中的深度差。接下来,通过右移操作将a移动到与b相同的深度,然后通过异或操作计算这两个同深度的节点的差异。这个差异的二进制表示中的1的个数表示了在同一层内,从一个节点到另一个节点需要经过的节点数。环的长度是由从a到b的路径长度加上额外的一条边组成的,因此总长度是a到b同层路径长度的两倍加上从a降到b的层的长度l再加上1(代表新增的边)。
时间复杂度:
O(m)
空间复杂度:
O(1)
代码细节讲解
🦆
为什么在处理查询时,需要将a和b中较大的值赋给a,这样的操作有什么特别的意义或优势吗?
▷🦆
在利用位运算计算两节点之间的路径长度时,为什么选择使用异或操作来确定从一个节点到另一个节点需要经过的节点数?
▷🦆
题解中提到的`深度差l`和右移操作如何确保a和b到达同一深度?这种方法在所有情况下都有效吗?
▷🦆
题解提到计算环的长度时,将`同层路径长度的两倍`加上`从a降到b的层的长度l`再加上1,为什么要将同层路径长度乘以两倍?
▷