使二叉树所有路径值相等的最小代价
难度:
标签:
题目描述
You are given an integer n representing the number of nodes in a perfect binary tree consisting of nodes numbered from 1 to n. The root of the tree is node 1 and each node i in the tree has two children where the left child is the node 2 * i and the right child is 2 * i + 1.
Each node in the tree also has a cost represented by a given 0-indexed integer array cost of size n where cost[i] is the cost of node i + 1. You are allowed to increment the cost of any node by 1 any number of times.
Return the minimum number of increments you need to make the cost of paths from the root to each leaf node equal.
Note:
- A perfect binary tree is a tree where each node, except the leaf nodes, has exactly 2 children.
- The cost of a path is the sum of costs of nodes in the path.
Example 1:
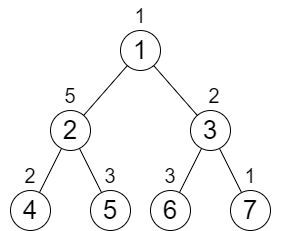
Input: n = 7, cost = [1,5,2,2,3,3,1] Output: 6 Explanation: We can do the following increments: - Increase the cost of node 4 one time. - Increase the cost of node 3 three times. - Increase the cost of node 7 two times. Each path from the root to a leaf will have a total cost of 9. The total increments we did is 1 + 3 + 2 = 6. It can be shown that this is the minimum answer we can achieve.
Example 2:
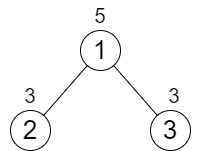
Input: n = 3, cost = [5,3,3] Output: 0 Explanation: The two paths already have equal total costs, so no increments are needed.
Constraints:
3 <= n <= 105n + 1is a power of2cost.length == n1 <= cost[i] <= 104
代码结果
运行时间: 107 ms, 内存: 23.6 MB
/*
* 题目思路:
* 1. 使用Java Stream API来计算从根到每个叶子节点的路径和。
* 2. 找到最大的路径和作为目标路径和。
* 3. 计算将路径和增加到目标路径和所需的最少操作次数。
*/
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class Solution {
public int minIncrements(int n, int[] cost) {
// 计算树的深度
int depth = (int) (Math.log(n + 1) / Math.log(2));
// 计算每个节点到根的路径和
int[] pathSums = IntStream.range(0, n).map(i -> {
int current = i + 1;
int sum = 0;
while (current > 0) {
sum += cost[current - 1];
current /= 2;
}
return sum;
}).toArray();
// 找到最大路径和
int maxPathSum = IntStream.of(pathSums).max().orElse(0);
// 计算需要的最小操作次数
return IntStream.of(pathSums).map(sum -> maxPathSum - sum).sum();
}
}解释
方法:
这个题解使用了自底向上的方法来确保所有从根到叶子的路径的值相等。算法从树的最底层(叶子节点)开始,逐层向上调整,使得每个非叶子节点的两个子节点的路径值相等。这是通过将较小的子节点的值增加到较大的子节点的值来实现的。每次操作完成后,将较大的子节点的值累加到父节点上。这样,父节点的值逐渐增加,直到达到根节点。这种方法保证了增加的总次数最小。
时间复杂度:
O(n)
空间复杂度:
O(1)
代码细节讲解
🦆
为什么这个题解选择从树的最底层叶子节点开始处理,而不是从根节点开始?
▷🦆
在判断左右子节点值大小并进行增加操作时,这种方法是否考虑了最终路径值可能因为逐层累加而导致过度增加的问题?
▷🦆
算法在每次处理节点对时,为何总是选择将较小值的节点调整到较大值,而不是考虑将两个节点的值都增加到某个中间值?
▷🦆
在实现中,更新父节点的值时,直接使用了子节点的较大值,这种做法是否有可能导致非最优解,即可能存在更小的增加次数的方案?
▷