矩阵中严格递增的单元格数
难度:
标签:
题目描述
Given a 1-indexed m x n integer matrix mat, you can select any cell in the matrix as your starting cell.
From the starting cell, you can move to any other cell in the same row or column, but only if the value of the destination cell is strictly greater than the value of the current cell. You can repeat this process as many times as possible, moving from cell to cell until you can no longer make any moves.
Your task is to find the maximum number of cells that you can visit in the matrix by starting from some cell.
Return an integer denoting the maximum number of cells that can be visited.
Example 1:
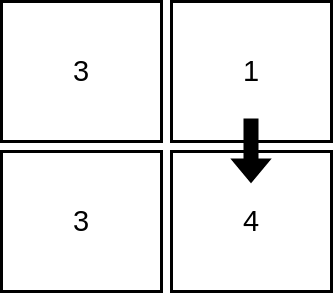
Input: mat = [[3,1],[3,4]] Output: 2 Explanation: The image shows how we can visit 2 cells starting from row 1, column 2. It can be shown that we cannot visit more than 2 cells no matter where we start from, so the answer is 2.
Example 2:
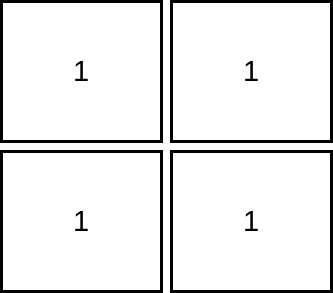
Input: mat = [[1,1],[1,1]] Output: 1 Explanation: Since the cells must be strictly increasing, we can only visit one cell in this example.
Example 3:
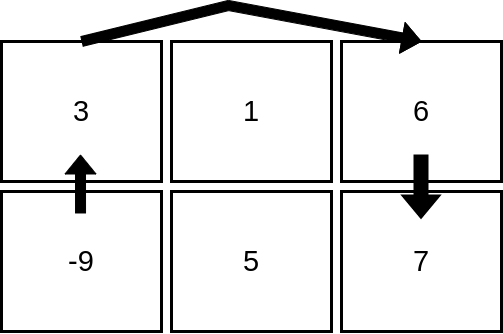
Input: mat = [[3,1,6],[-9,5,7]] Output: 4 Explanation: The image above shows how we can visit 4 cells starting from row 2, column 1. It can be shown that we cannot visit more than 4 cells no matter where we start from, so the answer is 4.
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1051 <= m * n <= 105-105 <= mat[i][j] <= 105
代码结果
运行时间: 704 ms, 内存: 54.7 MB
/*
思路:
1. 通过Java Stream来进行行和列的遍历。
2. 使用DFS(深度优先搜索)来找到从一个单元格开始能够访问的最大单元格数量。
3. 对于每一个单元格,检查其行和列中是否存在比其值更大的单元格。
4. 使用动态规划记录每个单元格的访问最大数量以避免重复计算。
*/
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class Solution {
private int m, n;
private int[][] mat;
private int[][] dp;
public int maxCells(int[][] mat) {
this.m = mat.length;
this.n = mat[0].length;
this.mat = mat;
this.dp = new int[m][n];
int maxCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
maxCount = Math.max(maxCount, dfs(i, j));
}
}
return maxCount;
}
private int dfs(int i, int j) {
if (dp[i][j] != 0) return dp[i][j];
int maxCount = 1;
IntStream.range(0, m).filter(x -> mat[x][j] > mat[i][j]).forEach(x -> {
maxCount = Math.max(maxCount, 1 + dfs(x, j));
});
IntStream.range(0, n).filter(y -> mat[i][y] > mat[i][j]).forEach(y -> {
maxCount = Math.max(maxCount, 1 + dfs(i, y));
});
dp[i][j] = maxCount;
return maxCount;
}
}解释
方法:
题解使用了动态规划和排序的方法来解决问题。首先,将矩阵中的所有单元格与它们的坐标一起存储到列表中,并按照单元格的值进行排序。接着,定义两个数组 rowMax 和 colMax 来存储每行和每列的最大可访问单元格数。通过遍历排序后的单元格列表,利用动态规划的思想,计算从每个单元格开始可以访问的最大单元格数量。如果当前单元格的值与前一个不同,则更新 rowMax 和 colMax。对于每个单元格,其可访问数是其所在行和列的最大可访问数中的最大值加一。最后,返回所有单元格的最大可访问数。
时间复杂度:
O(mn log(mn))
空间复杂度:
O(mn)
代码细节讲解
🦆
在题解中,为什么将所有单元格以它们的值进行排序?这个排序对解题思路有什么作用?
▷🦆
题解提到使用动态规划,能否详细解释动态规划在此问题中的具体应用和状态转移方程?
▷🦆
题解中提到更新rowMax和colMax数组,这个更新过程是如何确保不遗漏任何可能的路径的?
▷🦆
题解中使用了一个cache列表来临时存储数据,在什么情况下需要清空cache,并将其值更新到rowMax和colMax数组?
▷