访问所有节点的最短路径
难度:
标签:
题目描述
You have an undirected, connected graph of n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. You are given an array graph where graph[i] is a list of all the nodes connected with node i by an edge.
Return the length of the shortest path that visits every node. You may start and stop at any node, you may revisit nodes multiple times, and you may reuse edges.
Example 1:
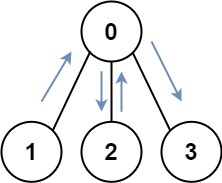
Input: graph = [[1,2,3],[0],[0],[0]] Output: 4 Explanation: One possible path is [1,0,2,0,3]
Example 2:
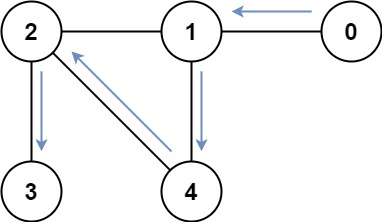
Input: graph = [[1],[0,2,4],[1,3,4],[2],[1,2]] Output: 4 Explanation: One possible path is [0,1,4,2,3]
Constraints:
n == graph.length1 <= n <= 120 <= graph[i].length < ngraph[i]does not containi.- If
graph[a]containsb, thengraph[b]containsa. - The input graph is always connected.
代码结果
运行时间: 101 ms, 内存: 17.7 MB
/*
* Problem Statement:
* Given an undirected connected graph with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1,
* represented as an array graph where graph[i] is a list of all nodes connected to node i.
* Return the length of the shortest path that visits every node. You may start and stop at any node.
*
* Approach:
* 1. Use Java Stream API along with BFS to explore all possible paths.
* 2. Maintain a queue to store the current node, visited nodes, and distance.
* 3. Use a bitmask to keep track of visited nodes.
* 4. Continue BFS until all nodes have been visited.
*/
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class ShortestPathStream {
public int shortestPathLength(int[][] graph) {
int n = graph.length;
int target = (1 << n) - 1; // bitmask representing all nodes visited
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][target + 1];
// Initialize the queue with all nodes
IntStream.range(0, n).forEach(i -> {
queue.offer(new int[]{i, 1 << i, 0});
visited[i][1 << i] = true;
});
// BFS
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] current = queue.poll();
int node = current[0];
int mask = current[1];
int dist = current[2];
// If all nodes are visited, return the distance
if (mask == target) return dist;
// Explore all neighbors
Arrays.stream(graph[node]).forEach(neighbor -> {
int nextMask = mask | (1 << neighbor);
if (!visited[neighbor][nextMask]) {
queue.offer(new int[]{neighbor, nextMask, dist + 1});
visited[neighbor][nextMask] = true;
}
});
}
return -1; // should never reach here
}
}
解释
方法:
该题解采用了广度优先搜索(BFS)结合位掩码技术来解决问题。每个节点的状态由节点编号和一个整数表示,这个整数的二进制表示中,每个位的开闭状态代表对应节点是否被访问过。初始化时,将每个节点自身作为起点,放入队列,并标记为已访问。然后进行层次遍历,每次从队列中取出节点和对应状态,检查是否所有节点都已访问(位掩码中所有位都为1),如果是,则返回当前步数作为答案。否则,将当前节点的所有邻居节点按新的访问状态加入队列,继续遍历。这种方法有效地遍历了所有可能的路径,并在找到最短路径时立即停止。
时间复杂度:
O(n^2 * 2^n)
空间复杂度:
O(n * 2^n)
代码细节讲解
🦆
在题解中使用位掩码表示节点的访问状态,这种方法相比其他方法有什么优势?
▷🦆
为什么在遍历过程中,一旦发现某个状态下的位掩码表示所有节点都已访问,就可以立即返回当前步数作为答案?
▷🦆
题解中提到,初始化时将每个节点自身作为起点放入队列,这样的初始化方式是基于什么考量?
▷