在矩阵上写出字母 Y 所需的最少操作次数
难度:
标签:
题目描述
You are given a 0-indexed n x n grid where n is odd, and grid[r][c] is 0, 1, or 2.
We say that a cell belongs to the Letter Y if it belongs to one of the following:
- The diagonal starting at the top-left cell and ending at the center cell of the grid.
- The diagonal starting at the top-right cell and ending at the center cell of the grid.
- The vertical line starting at the center cell and ending at the bottom border of the grid.
The Letter Y is written on the grid if and only if:
- All values at cells belonging to the Y are equal.
- All values at cells not belonging to the Y are equal.
- The values at cells belonging to the Y are different from the values at cells not belonging to the Y.
Return the minimum number of operations needed to write the letter Y on the grid given that in one operation you can change the value at any cell to 0, 1, or 2.
Example 1:
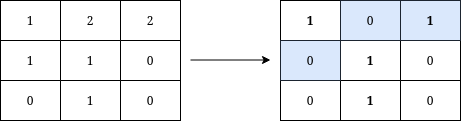
Input: grid = [[1,2,2],[1,1,0],[0,1,0]] Output: 3 Explanation: We can write Y on the grid by applying the changes highlighted in blue in the image above. After the operations, all cells that belong to Y, denoted in bold, have the same value of 1 while those that do not belong to Y are equal to 0. It can be shown that 3 is the minimum number of operations needed to write Y on the grid.
Example 2:
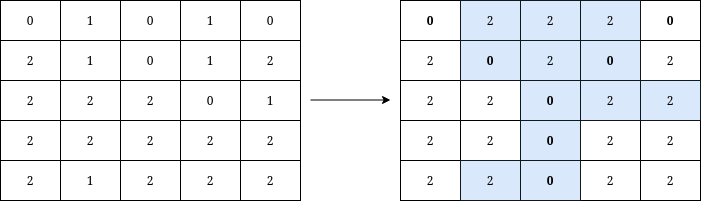
Input: grid = [[0,1,0,1,0],[2,1,0,1,2],[2,2,2,0,1],[2,2,2,2,2],[2,1,2,2,2]] Output: 12 Explanation: We can write Y on the grid by applying the changes highlighted in blue in the image above. After the operations, all cells that belong to Y, denoted in bold, have the same value of 0 while those that do not belong to Y are equal to 2. It can be shown that 12 is the minimum number of operations needed to write Y on the grid.
Constraints:
3 <= n <= 49n == grid.length == grid[i].length0 <= grid[i][j] <= 2nis odd.
代码结果
运行时间: 43 ms, 内存: 16.2 MB
/*
* 思路:
* 1. 找出矩阵的中心点。
* 2. 使用流处理来记录Y字母形状所需的坐标。
* 3. 计算当前属于Y形状的单元格和非Y形状的单元格的值。
* 4. 计算将这些单元格转换为目标值所需的操作次数。
* 5. 返回最少的操作次数。
*/
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class Solution {
public int minOperations(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int center = n / 2;
List<int[]> yCells = IntStream.range(0, center + 1)
.flatMap(i -> Stream.of(new int[]{i, i}, new int[]{i, n - 1 - i}))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
yCells.addAll(IntStream.range(center, n).mapToObj(i -> new int[]{i, center}).collect(Collectors.toList()));
Set<Integer> yValues = yCells.stream().map(cell -> grid[cell[0]][cell[1]]).collect(Collectors.toSet());
Set<Integer> nonYValues = IntStream.range(0, n).boxed()
.flatMap(i -> IntStream.range(0, n).mapToObj(j -> new int[]{i, j}))
.filter(cell -> !yCells.contains(cell))
.map(cell -> grid[cell[0]][cell[1]]).collect(Collectors.toSet());
return yValues.stream().flatMapToInt(yValue -> nonYValues.stream()
.filter(nonYValue -> yValue != nonYValue)
.mapToInt(nonYValue -> (int) yCells.stream().filter(cell -> grid[cell[0]][cell[1]] != yValue).count() +
(int) IntStream.range(0, n).boxed()
.flatMap(i -> IntStream.range(0, n).mapToObj(j -> new int[]{i, j}))
.filter(cell -> !yCells.contains(cell) && grid[cell[0]][cell[1]] != nonYValue)
.count())).min().orElse(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
}解释
方法:
此题的解法是通过统计属于Y形的单元格和非Y形的单元格中0、1、2的出现次数,然后尝试所有可能的值组合来最小化变换次数。首先使用两个计数器cnt1和cnt2分别统计属于Y的单元格和不属于Y的单元格中0、1、2的出现次数。接着,对于每种可能的Y值(0、1、2)和非Y值(也是0、1、2),当Y值不等于非Y值时,计算不需要变化的单元格数量(即已经为目标值的单元格数量)。最后,从总单元格数中减去这个最大的不需要变化的单元格数量,得到最小的操作次数。
时间复杂度:
O(n^2)
空间复杂度:
O(1)
代码细节讲解
🦆
如何确定哪些单元格属于Y形的一部分以及哪些不属于?代码中具体的判断逻辑是什么?
▷🦆
在计算操作次数时,为什么要尝试所有可能的Y值和非Y值组合,而不是直接选取出现次数最多的值作为目标值?
▷🦆
对于中心单元格,它似乎在代码中被重复计算了两次(一次在上半部分,一次在下半部分的垂直线),这样处理是否正确?
▷