将节点分成尽可能多的组
难度:
标签:
题目描述
You are given a positive integer n representing the number of nodes in an undirected graph. The nodes are labeled from 1 to n.
You are also given a 2D integer array edges, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is a bidirectional edge between nodes ai and bi. Notice that the given graph may be disconnected.
Divide the nodes of the graph into m groups (1-indexed) such that:
- Each node in the graph belongs to exactly one group.
- For every pair of nodes in the graph that are connected by an edge
[ai, bi], ifaibelongs to the group with indexx, andbibelongs to the group with indexy, then|y - x| = 1.
Return the maximum number of groups (i.e., maximum m) into which you can divide the nodes. Return -1 if it is impossible to group the nodes with the given conditions.
Example 1:
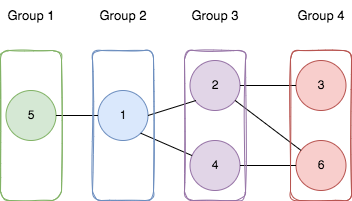
Input: n = 6, edges = [[1,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,6],[2,3],[4,6]] Output: 4 Explanation: As shown in the image we: - Add node 5 to the first group. - Add node 1 to the second group. - Add nodes 2 and 4 to the third group. - Add nodes 3 and 6 to the fourth group. We can see that every edge is satisfied. It can be shown that that if we create a fifth group and move any node from the third or fourth group to it, at least on of the edges will not be satisfied.
Example 2:
Input: n = 3, edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,1]] Output: -1 Explanation: If we add node 1 to the first group, node 2 to the second group, and node 3 to the third group to satisfy the first two edges, we can see that the third edge will not be satisfied. It can be shown that no grouping is possible.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 5001 <= edges.length <= 104edges[i].length == 21 <= ai, bi <= nai != bi- There is at most one edge between any pair of vertices.
代码结果
运行时间: 552 ms, 内存: 18.7 MB
/*
* 思路:
* 1. 使用 Java Streams 和 BFS 进行分组。
* 2. 如果图是二分图,则最多可以分为两组。如果不是,返回 -1。
* 3. 通过 BFS 和流操作尝试将节点染色(0 或 1)。
* 4. 如果在染色过程中发现同一条边的两个节点被染成相同的颜色,说明图不是二分图,返回 -1。
*/
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.*;
public class Solution {
public int maxGroups(int n, int[][] edges) {
List<List<Integer>> graph = IntStream.range(0, n)
.mapToObj(i -> new ArrayList<Integer>())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
Arrays.stream(edges).forEach(edge -> {
graph.get(edge[0] - 1).add(edge[1] - 1);
graph.get(edge[1] - 1).add(edge[0] - 1);
});
int[] color = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(color, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (color[i] == -1) {
if (!bfs(graph, color, i)) {
return -1;
}
}
}
return 2;
}
private boolean bfs(List<List<Integer>> graph, int[] color, int start) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(start);
color[start] = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int node = queue.poll();
for (int neighbor : graph.get(node)) {
if (color[neighbor] == -1) {
color[neighbor] = color[node] ^ 1;
queue.offer(neighbor);
} else if (color[neighbor] == color[node]) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
解释
方法:
该题解通过将问题转化为二分图检测来解决。步骤如下:
1. 构建图的邻接列表。
2. 使用颜色数组 `color` 来检测图是否为二分图。二分图可以被分成两组,其中任何一条边的两个顶点都属于不同的组。
3. 为每个未染色的节点尝试进行二分图染色,使用深度优先搜索(DFS)。如果发现某个节点及其相邻节点颜色相同,说明存在奇数环,返回-1。
4. 对每个连通分量使用广度优先搜索(BFS)来确定其深度,深度决定了可以分的组数。
5. 计算所有连通分量的深度和作为最终结果。
时间复杂度:
O(V+E)
空间复杂度:
O(V+E)
代码细节讲解
🦆
为什么在确定是否为二分图时,需要使用颜色数组标记节点,并选择颜色值为正负号?
▷🦆
在二分图检测的代码中,当发现一个节点及其相邻节点颜色相同时,直接返回-1,这样的处理是否意味着整个图中存在奇数环?
▷🦆
在进行BFS以计算连通分量的深度时,为什么需要一个额外的数组`time`来标记节点是否已经被访问?
▷