边权重均等查询
难度:
标签:
题目描述
There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. You are given the integer n and a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ui and vi with weight wi in the tree.
You are also given a 2D integer array queries of length m, where queries[i] = [ai, bi]. For each query, find the minimum number of operations required to make the weight of every edge on the path from ai to bi equal. In one operation, you can choose any edge of the tree and change its weight to any value.
Note that:
- Queries are independent of each other, meaning that the tree returns to its initial state on each new query.
- The path from
aitobiis a sequence of distinct nodes starting with nodeaiand ending with nodebisuch that every two adjacent nodes in the sequence share an edge in the tree.
Return an array answer of length m where answer[i] is the answer to the ith query.
Example 1:
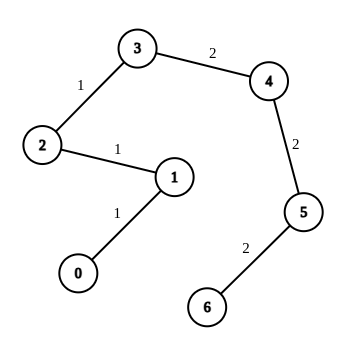
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,1],[3,4,2],[4,5,2],[5,6,2]], queries = [[0,3],[3,6],[2,6],[0,6]] Output: [0,0,1,3] Explanation: In the first query, all the edges in the path from 0 to 3 have a weight of 1. Hence, the answer is 0. In the second query, all the edges in the path from 3 to 6 have a weight of 2. Hence, the answer is 0. In the third query, we change the weight of edge [2,3] to 2. After this operation, all the edges in the path from 2 to 6 have a weight of 2. Hence, the answer is 1. In the fourth query, we change the weights of edges [0,1], [1,2] and [2,3] to 2. After these operations, all the edges in the path from 0 to 6 have a weight of 2. Hence, the answer is 3. For each queries[i], it can be shown that answer[i] is the minimum number of operations needed to equalize all the edge weights in the path from ai to bi.
Example 2:
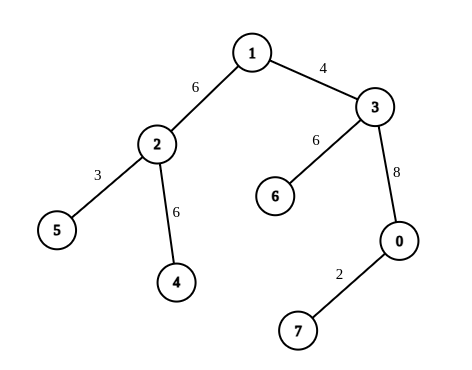
Input: n = 8, edges = [[1,2,6],[1,3,4],[2,4,6],[2,5,3],[3,6,6],[3,0,8],[7,0,2]], queries = [[4,6],[0,4],[6,5],[7,4]] Output: [1,2,2,3] Explanation: In the first query, we change the weight of edge [1,3] to 6. After this operation, all the edges in the path from 4 to 6 have a weight of 6. Hence, the answer is 1. In the second query, we change the weight of edges [0,3] and [3,1] to 6. After these operations, all the edges in the path from 0 to 4 have a weight of 6. Hence, the answer is 2. In the third query, we change the weight of edges [1,3] and [5,2] to 6. After these operations, all the edges in the path from 6 to 5 have a weight of 6. Hence, the answer is 2. In the fourth query, we change the weights of edges [0,7], [0,3] and [1,3] to 6. After these operations, all the edges in the path from 7 to 4 have a weight of 6. Hence, the answer is 3. For each queries[i], it can be shown that answer[i] is the minimum number of operations needed to equalize all the edge weights in the path from ai to bi.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 104edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 30 <= ui, vi < n1 <= wi <= 26- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree. 1 <= queries.length == m <= 2 * 104queries[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < n
代码结果
运行时间: 1250 ms, 内存: 40.6 MB
/*
思路:
1. 使用DFS或BFS找到从ai到bi的路径。
2. 统计路径上每个边权重的出现次数。
3. 计算最小的操作次数,使得路径上的所有边权重相等。
*/
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class SolutionStream {
public int[] minOperationsToEqualWeights(int n, int[][] edges, int[][] queries) {
List<int[]>[] graph = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int[] edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0], v = edge[1], w = edge[2];
graph[u].add(new int[]{v, w});
graph[v].add(new int[]{u, w});
}
return Arrays.stream(queries).mapToInt(query -> minOperations(query[0], query[1], graph, n)).toArray();
}
private int minOperations(int a, int b, List<int[]>[] graph, int n) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
Map<Integer, Integer> weightCount = new HashMap<>();
dfs(a, b, graph, visited, weightCount);
int maxCount = weightCount.values().stream().max(Integer::compare).orElse(0);
return weightCount.values().stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum() - maxCount;
}
private boolean dfs(int current, int target, List<int[]>[] graph, boolean[] visited, Map<Integer, Integer> weightCount) {
if (current == target) return true;
visited[current] = true;
for (int[] neighbor : graph[current]) {
int nextNode = neighbor[0], weight = neighbor[1];
if (!visited[nextNode]) {
weightCount.put(weight, weightCount.getOrDefault(weight, 0) + 1);
if (dfs(nextNode, target, graph, visited, weightCount)) {
return true;
}
weightCount.put(weight, weightCount.get(weight) - 1);
}
}
return false;
}
}解释
方法:
这个题解利用了图的遍历和并查集以及路径压缩的技术来找到查询中两个节点的最小公共祖先(LCA)。首先,构建了一个邻接表g来表示图,用字典存储边的权重。使用并查集来帮助找到每个节点的根节点,并在遍历过程中动态更新根节点。同时使用深度优先搜索(DFS)来计算每个节点到根节点的路径上各个权重的数量。通过比较路径上的权重来确定最小的操作次数,以使得从节点ai到bi的路径上的所有边权重相等。具体来说,对于每个查询,计算两个节点到它们的LCA的路径长度,再根据权重计数数组,找出需要改变最少的边数使得整个路径的权重一致。
时间复杂度:
O((n + m) * alpha(n))
空间复杂度:
O(n)
代码细节讲解
🦆
在并查集中,如何通过路径压缩技术优化查找操作的效率?
▷🦆
题解中提到使用深度优先搜索(DFS)来计算权重计数数组,这个数组具体是如何定义和更新的?
▷🦆
题解利用Tarjan算法找到最小公共祖先(LCA),请问在这种应用中Tarjan算法的基本工作原理是什么?
▷