二叉树的堂兄弟节点 II
难度:
标签:
题目描述
Given the root of a binary tree, replace the value of each node in the tree with the sum of all its cousins' values.
Two nodes of a binary tree are cousins if they have the same depth with different parents.
Return the root of the modified tree.
Note that the depth of a node is the number of edges in the path from the root node to it.
Example 1:
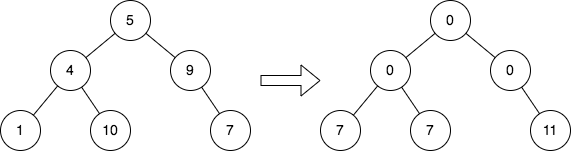
Input: root = [5,4,9,1,10,null,7] Output: [0,0,0,7,7,null,11] Explanation: The diagram above shows the initial binary tree and the binary tree after changing the value of each node. - Node with value 5 does not have any cousins so its sum is 0. - Node with value 4 does not have any cousins so its sum is 0. - Node with value 9 does not have any cousins so its sum is 0. - Node with value 1 has a cousin with value 7 so its sum is 7. - Node with value 10 has a cousin with value 7 so its sum is 7. - Node with value 7 has cousins with values 1 and 10 so its sum is 11.
Example 2:
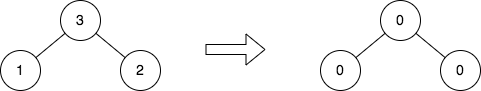
Input: root = [3,1,2] Output: [0,0,0] Explanation: The diagram above shows the initial binary tree and the binary tree after changing the value of each node. - Node with value 3 does not have any cousins so its sum is 0. - Node with value 1 does not have any cousins so its sum is 0. - Node with value 2 does not have any cousins so its sum is 0.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 104
代码结果
运行时间: 319 ms, 内存: 54.9 MB
/*
* 题目思路:
* 1. 使用Java Stream API实现堂兄弟节点值和的计算。
* 2. 遍历每层节点,使用Map存储每层的节点信息。
* 3. 对于每个节点,计算堂兄弟节点的和,更新节点的值。
*/
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
public class Solution {
public TreeNode replaceCousinSum(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return null;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int levelSize = queue.size();
List<TreeNode> nodes = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
nodes.add(node);
if (node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);
}
int levelSum = nodes.stream().mapToInt(n -> n.val).sum();
nodes.forEach(node -> {
int siblingSum = (node.left != null ? node.left.val : 0) + (node.right != null ? node.right.val : 0);
node.val = levelSum - siblingSum;
});
}
return root;
}
}解释
方法:
该题解采用了深度优先搜索算法(DFS)来解决问题。分为两个主要步骤:
1. 首先,通过第一个DFS(函数dfs1)遍历整棵树并计算出每一层所有节点值的总和,这些总和保存在dSum列表中。每个索引i对应的dSum[i]表示第i层所有节点的值的总和。
2. 第二个DFS(函数dfs2)用于更新每个节点的值。在这个阶段,对于每个节点,我们计算其所有堂兄弟节点值的总和。这通过从当前层总和中减去该节点直接子节点的值来实现。这种计算保证了节点值被替换为所有堂兄弟的值的和。
整个过程确保了每个节点都被正确地替换为其堂兄弟节点的值之和,满足题目要求。
时间复杂度:
O(n)
空间复杂度:
O(n)
代码细节讲解
🦆
在第一个DFS函数中,你是如何确保`dSum`列表准确地记录了每一层节点的总和?特别是当存在不平衡树时。
▷🦆
在第二个DFS函数中,为什么直接从`dSum[depth]`中减去当前节点的子节点值来更新其值?这样做是否能确保当前节点的值正确地反映了所有堂兄弟节点的总和?
▷🦆
在处理节点值替换时,根节点的值为什么被设置为0?这是否意味着根节点没有堂兄弟节点?
▷