有向图访问计数
难度:
标签:
题目描述
There is a directed graph consisting of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 and n directed edges.
You are given a 0-indexed array edges where edges[i] indicates that there is an edge from node i to node edges[i].
Consider the following process on the graph:
- You start from a node
xand keep visiting other nodes through edges until you reach a node that you have already visited before on this same process.
Return an array answer where answer[i] is the number of different nodes that you will visit if you perform the process starting from node i.
Example 1:
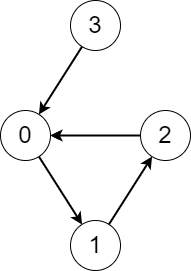
Input: edges = [1,2,0,0] Output: [3,3,3,4] Explanation: We perform the process starting from each node in the following way: - Starting from node 0, we visit the nodes 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 0. The number of different nodes we visit is 3. - Starting from node 1, we visit the nodes 1 -> 2 -> 0 -> 1. The number of different nodes we visit is 3. - Starting from node 2, we visit the nodes 2 -> 0 -> 1 -> 2. The number of different nodes we visit is 3. - Starting from node 3, we visit the nodes 3 -> 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 0. The number of different nodes we visit is 4.
Example 2:
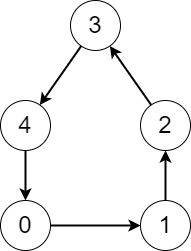
Input: edges = [1,2,3,4,0] Output: [5,5,5,5,5] Explanation: Starting from any node we can visit every node in the graph in the process.
Constraints:
n == edges.length2 <= n <= 1050 <= edges[i] <= n - 1edges[i] != i
代码结果
运行时间: 249 ms, 内存: 92.6 MB
/*
* Problem Description:
* Given a directed graph with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, and an array edges,
* where edges[i] represents a directed edge from node i to node edges[i].
* For each node, determine the number of unique nodes that can be visited starting from that node
* until a node is revisited in the process.
*
* Approach:
* - We use a stream to create a range of integers representing each node.
* - For each node, we calculate the number of unique nodes visited using a HashSet.
*/
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class GraphTraversalStream {
public int[] countUniqueNodes(int[] edges) {
return IntStream.range(0, edges.length)
.map(i -> {
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
int current = i;
while (visited.add(current)) {
current = edges[current];
}
return visited.size();
})
.toArray();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphTraversalStream gts = new GraphTraversalStream();
int[] edges1 = {1, 2, 0, 0};
int[] edges2 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 0};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(gts.countUniqueNodes(edges1))); // Output: [3, 3, 3, 4]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(gts.countUniqueNodes(edges2))); // Output: [5, 5, 5, 5, 5]
}
}解释
方法:
该题解使用了深度优先搜索(DFS)来探索图,并借助额外的数组来存储每个节点开始的遍历信息。从每个节点开始,使用DFS遍历直到遇到已访问的节点,从而检测出环。\n\n1. 使用`ans`数组存储每个节点开始的遍历可以访问的不同节点数。\n2. 使用`depth`数组记录每个节点在当前DFS路径的深度。\n3. `fixRing`函数用于更新在环中的所有节点的访问节点数。\n4. `dfs`函数用于深度优先搜索,它检查下一个节点是否已被解决(即`ans[nextNode] > 0`),或者是否已在当前路径上访问过以形成环(即`depth[nextNode] > 0`)。根据情况,更新当前节点的访问节点数或调用`fixRing`函数。\n5. 主循环确保从每个尚未解决的节点开始DFS。\n\n通过这种方式,每个节点的访问计数被逐步建立,直到图中所有节点的访问计数都被确定。
时间复杂度:
O(n)
空间复杂度:
O(n)
代码细节讲解
🦆
在`dfs`函数中,当遇到已被访问的节点时,如何确保不会错误地重复计数或错过某些节点的计数?
▷🦆
题解中提到使用`depth`数组记录每个节点在当前DFS路径的深度,这样的机制是如何帮助检测环的存在以及确定环的长度的?
▷🦆
函数`fixRing`被设计来更新环中每个节点的访问节点数,那么在更新过程中如何保证不会对环外的节点造成影响?
▷🦆
在题解的描述中,如果存在多个环或者环交叉的复杂情况,该算法是否仍然有效?具体是如何处理这种情况的?
▷