设计可以求最短路径的图类
难度:
标签:
题目描述
There is a directed weighted graph that consists of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. The edges of the graph are initially represented by the given array edges where edges[i] = [fromi, toi, edgeCosti] meaning that there is an edge from fromi to toi with the cost edgeCosti.
Implement the Graph class:
Graph(int n, int[][] edges)initializes the object withnnodes and the given edges.addEdge(int[] edge)adds an edge to the list of edges whereedge = [from, to, edgeCost]. It is guaranteed that there is no edge between the two nodes before adding this one.int shortestPath(int node1, int node2)returns the minimum cost of a path fromnode1tonode2. If no path exists, return-1. The cost of a path is the sum of the costs of the edges in the path.
Example 1:
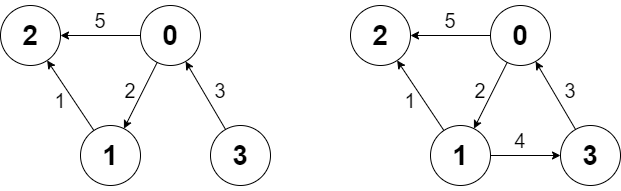
Input ["Graph", "shortestPath", "shortestPath", "addEdge", "shortestPath"] [[4, [[0, 2, 5], [0, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [3, 0, 3]]], [3, 2], [0, 3], [[1, 3, 4]], [0, 3]] Output [null, 6, -1, null, 6] Explanation Graph g = new Graph(4, [[0, 2, 5], [0, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [3, 0, 3]]); g.shortestPath(3, 2); // return 6. The shortest path from 3 to 2 in the first diagram above is 3 -> 0 -> 1 -> 2 with a total cost of 3 + 2 + 1 = 6. g.shortestPath(0, 3); // return -1. There is no path from 0 to 3. g.addEdge([1, 3, 4]); // We add an edge from node 1 to node 3, and we get the second diagram above. g.shortestPath(0, 3); // return 6. The shortest path from 0 to 3 now is 0 -> 1 -> 3 with a total cost of 2 + 4 = 6.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1000 <= edges.length <= n * (n - 1)edges[i].length == edge.length == 30 <= fromi, toi, from, to, node1, node2 <= n - 11 <= edgeCosti, edgeCost <= 106- There are no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph at any point.
- At most
100calls will be made foraddEdge. - At most
100calls will be made forshortestPath.
代码结果
运行时间: 237 ms, 内存: 19.1 MB
/*
题目思路:
1. 使用Dijkstra算法求解最短路径。
2. 使用一个邻接表存储图的边和权重。
3. 初始化Graph类时,填充邻接表。
4. addEdge方法用于在邻接表中添加新的边。
5. shortestPath方法使用Dijkstra算法计算从node1到node2的最短路径。
*/
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.*;
class Graph {
private Map<Integer, List<int[]>> graph;
private int n;
public Graph(int n, int[][] edges) {
this.n = n;
graph = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph.put(i, new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int[] edge : edges) {
graph.get(edge[0]).add(new int[]{edge[1], edge[2]});
}
}
public void addEdge(int[] edge) {
graph.get(edge[0]).add(new int[]{edge[1], edge[2]});
}
public int shortestPath(int node1, int node2) {
int[] dist = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
dist[node1] = 0;
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[1]));
pq.offer(new int[]{node1, 0});
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int[] current = pq.poll();
int u = current[0];
int d = current[1];
if (u == node2) return d;
for (int[] neighbor : graph.get(u)) {
int v = neighbor[0];
int weight = neighbor[1];
if (dist[v] > d + weight) {
dist[v] = d + weight;
pq.offer(new int[]{v, dist[v]});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
解释
方法:
The solution implements a graph class with methods to initialize the graph, add edges, and compute the shortest path between two nodes using Dijkstra's algorithm. The graph is represented as an adjacency list, where each node points to a list of tuples, each containing a connected node and the edge weight. The `addEdge` method appends a new edge to the adjacency list. The `shortestPath` method applies Dijkstra's algorithm using a priority queue (min-heap) to efficiently find the shortest path by continually expanding the least costly path until the destination is reached or all possible paths are considered.
时间复杂度:
O(E log V)
空间复杂度:
O(V + E)
代码细节讲解
🦆
在实现Dijkstra算法时,你是如何处理图中可能存在的负权边?
▷🦆
为什么选择使用优先队列(最小堆)来实现Dijkstra算法?使用普通队列会有什么问题或效率差异?
▷🦆
请问在`shortestPath`方法中,`dist[start] = 0`这一初始化操作的目的是什么?
▷🦆
在算法中,当检查到`w0 > dist[y0]`时选择继续循环的逻辑是基于什么考虑?
▷