最大二叉树 II
难度:
标签:
题目描述
A maximum tree is a tree where every node has a value greater than any other value in its subtree.
You are given the root of a maximum binary tree and an integer val.
Just as in the previous problem, the given tree was constructed from a list a (root = Construct(a)) recursively with the following Construct(a) routine:
- If
ais empty, returnnull. - Otherwise, let
a[i]be the largest element ofa. Create arootnode with the valuea[i]. - The left child of
rootwill beConstruct([a[0], a[1], ..., a[i - 1]]). - The right child of
rootwill beConstruct([a[i + 1], a[i + 2], ..., a[a.length - 1]]). - Return
root.
Note that we were not given a directly, only a root node root = Construct(a).
Suppose b is a copy of a with the value val appended to it. It is guaranteed that b has unique values.
Return Construct(b).
Example 1:
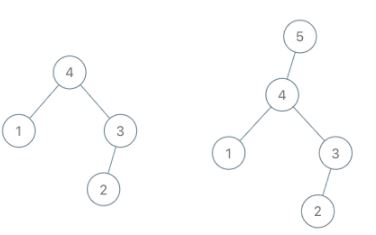
Input: root = [4,1,3,null,null,2], val = 5 Output: [5,4,null,1,3,null,null,2] Explanation: a = [1,4,2,3], b = [1,4,2,3,5]
Example 2:
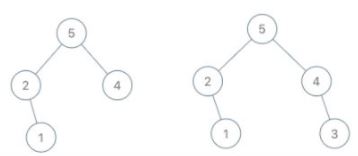
Input: root = [5,2,4,null,1], val = 3 Output: [5,2,4,null,1,null,3] Explanation: a = [2,1,5,4], b = [2,1,5,4,3]
Example 3:

Input: root = [5,2,3,null,1], val = 4 Output: [5,2,4,null,1,3] Explanation: a = [2,1,5,3], b = [2,1,5,3,4]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 100]. 1 <= Node.val <= 100- All the values of the tree are unique.
1 <= val <= 100
代码结果
运行时间: 24 ms, 内存: 16.0 MB
/*
* 思路:
* 1. 使用Stream进行遍历和插入操作。
* 2. 与传统方法类似,但利用了Stream API的简洁性。
*/
import java.util.stream.Stream;
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
public class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoMaxTree(TreeNode root, int val) {
return insert(root, val);
}
private TreeNode insert(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null) return new TreeNode(val);
return Stream.of(root)
.filter(node -> val > node.val)
.map(node -> {
TreeNode newNode = new TreeNode(val);
newNode.left = node;
return newNode;
})
.findFirst()
.orElseGet(() -> {
root.right = insert(root.right, val);
return root;
});
}
}解释
方法:
该题解采用递归的方式插入新值到最大二叉树中。如果当前根节点为空,则直接返回新建立的节点;如果插入的值大于当前根节点的值,则新值将成为新的根节点,并且原来的树作为新根节点的左子树;如果插入的值小于或等于当前根节点的值,则递归地将新值插入到当前根节点的右子树中。
时间复杂度:
O(n)
空间复杂度:
O(n)
代码细节讲解
🦆
在插入操作中,如果插入的值小于或等于当前根节点的值,新值是如何保证一直保持最大二叉树的特性的?
▷🦆
如果新值需要插入到树的最右侧,会不会影响到树的平衡性?如果是,这个问题如何解决?
▷🦆
为什么插入一个新值时,新值大于根节点的值就必须使得新值成为新的根节点,并且把原树作为左子树?这样的操作有什么特定的优势吗?
▷相关问题
最大二叉树
给定一个不重复的整数数组 nums 。 最大二叉树 可以用下面的算法从 nums 递归地构建:
- 创建一个根节点,其值为
nums中的最大值。 - 递归地在最大值 左边 的 子数组前缀上 构建左子树。
- 递归地在最大值 右边 的 子数组后缀上 构建右子树。
返回 nums 构建的 最大二叉树 。
示例 1:

输入:nums = [3,2,1,6,0,5]
输出:[6,3,5,null,2,0,null,null,1]
解释:递归调用如下所示:
- [3,2,1,6,0,5] 中的最大值是 6 ,左边部分是 [3,2,1] ,右边部分是 [0,5] 。
- [3,2,1] 中的最大值是 3 ,左边部分是 [] ,右边部分是 [2,1] 。
- 空数组,无子节点。
- [2,1] 中的最大值是 2 ,左边部分是 [] ,右边部分是 [1] 。
- 空数组,无子节点。
- 只有一个元素,所以子节点是一个值为 1 的节点。
- [0,5] 中的最大值是 5 ,左边部分是 [0] ,右边部分是 [] 。
- 只有一个元素,所以子节点是一个值为 0 的节点。
- 空数组,无子节点。
示例 2:

输入:nums = [3,2,1] 输出:[3,null,2,null,1]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10000 <= nums[i] <= 1000nums中的所有整数 互不相同