矩阵查询可获得的最大分数
难度:
标签:
题目描述
You are given an m x n integer matrix grid and an array queries of size k.
Find an array answer of size k such that for each integer queries[i] you start in the top left cell of the matrix and repeat the following process:
- If
queries[i]is strictly greater than the value of the current cell that you are in, then you get one point if it is your first time visiting this cell, and you can move to any adjacent cell in all4directions: up, down, left, and right. - Otherwise, you do not get any points, and you end this process.
After the process, answer[i] is the maximum number of points you can get. Note that for each query you are allowed to visit the same cell multiple times.
Return the resulting array answer.
Example 1:
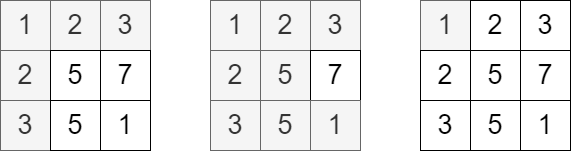
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[2,5,7],[3,5,1]], queries = [5,6,2] Output: [5,8,1] Explanation: The diagrams above show which cells we visit to get points for each query.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[5,2,1],[1,1,2]], queries = [3] Output: [0] Explanation: We can not get any points because the value of the top left cell is already greater than or equal to 3.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length2 <= m, n <= 10004 <= m * n <= 105k == queries.length1 <= k <= 1041 <= grid[i][j], queries[i] <= 106
代码结果
运行时间: 416 ms, 内存: 26.9 MB
// Java Stream solution
// Idea: Java Stream API is not well-suited for this problem since it involves DFS traversal with state tracking.
// However, we can use Stream to initialize the result array and then fill it using traditional loops.
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class Solution {
public int[] maxScores(int[][] grid, int[] queries) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int[] answer = IntStream.of(queries).map(q -> dfs(grid, q, m, n)).toArray();
return answer;
}
private int dfs(int[][] grid, int query, int m, int n) {
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
return dfsHelper(grid, query, 0, 0, visited);
}
private int dfsHelper(int[][] grid, int query, int x, int y, boolean[][] visited) {
if (x < 0 || x >= grid.length || y < 0 || y >= grid[0].length || visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] >= query) {
return 0;
}
visited[x][y] = true;
int score = 1;
int[][] directions = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
for (int[] dir : directions) {
score += dfsHelper(grid, query, x + dir[0], y + dir[1], visited);
}
return score;
}
}
解释
方法:
这个题解采用了优先队列(最小堆)的方式来实现。首先,初始化一个优先队列,将左上角的单元格作为起始点加入队列,并将其值标记为-1(已访问)。对于每个查询值,按照大小排序来处理。处理查询时,如果队列的顶部元素(当前值最小的元素)小于查询值,从队列中取出该元素,并探索其四个方向的相邻单元格。如果相邻单元格的值有效且未被访问,则将其加入队列,并将值设为-1。每次从队列中取出元素时,计数器递增,表示获得了分数。队列中的元素代表可以继续探索的单元格,只要其值小于当前查询值。最后,将计数器的值存入结果数组,该值即为当前查询所能获得的最大分数。
时间复杂度:
O((m*n) * log(m*n) + k log k)
空间复杂度:
O(m*n)
代码细节讲解
🦆
为什么在处理每个查询之前需要将查询进行排序?排序对算法的效率和结果有什么影响?
▷🦆
在优先队列中,使用元素的值作为比较基准来进行排序和弹出,这样的选择是否最优?是否有其他可能更有效的属性或方法?
▷🦆
在题解中提到,如果相邻单元格的值有效且未被访问,则将其加入队列。这里的'有效'是指什么?具体如何定义?
▷